Yan Jianyuan
University Library
Nankai University
Tianjin, China 300071
Abstract: Using the theory and method of Analytic Hierarchy Process(AHP) and integrating it with the evaluation target of the computer integrated system for library management, the author makes a lot of quantitative analysis for the problem of intro-
ducing and selecting the CISLM, and at last provides an AHP model for optimizing the scheme, so that an effective auxiliary decision method for the library automation could be found.
The computer integrated system for library management (CISLM) is a complicated system which concerns the function of library management, the performance of the system hardware and software, and the investment for the system. During the development of library automation, there are several schemes and targets in selecting and introducing the scheme of the library integrated system. The problem of which one to choose is decided by optimizing decisions. Since in the factors connected with the integrated system there exist many interactions and contradictions which are only qualitative targets. This brings a lot of difficulty to the user's subjective judgement and decision. The author thinks the main problem of optimizing and introducing an integrated system is that first, we must have a systematic evaluation target system which is practical, and second, we must have a set of scientific auxiliary decision methods. AHP is a convenient way for quantitative analysis to unquantitative matters in system engineering, it is also an effective method for people to objectively subscribe the subjective judgement. The author uses the AHP method to analyze the library integrated system scheme of a library in order that an effective target system and an auxiliary decision method can be found.
2. THE ANALYTIC HIERARCHY MODEL FOR OPTIMIZATION OF THE INTEGRATED SYSTEM
Using AHP to solve the problem, first we must make the problem hierarchic, separate it into several different factors according to its quality and target, and then group the factors into several levels according to their mutual influence and their subordinate relationship in order to form a multi-hierarchy analysis model, and, finally, sum up the system analysis as the determination of the weight which represents the importance of the lowest level (the scheme for decision) relative to the highest level (system target) or as the queuing process of system quality.
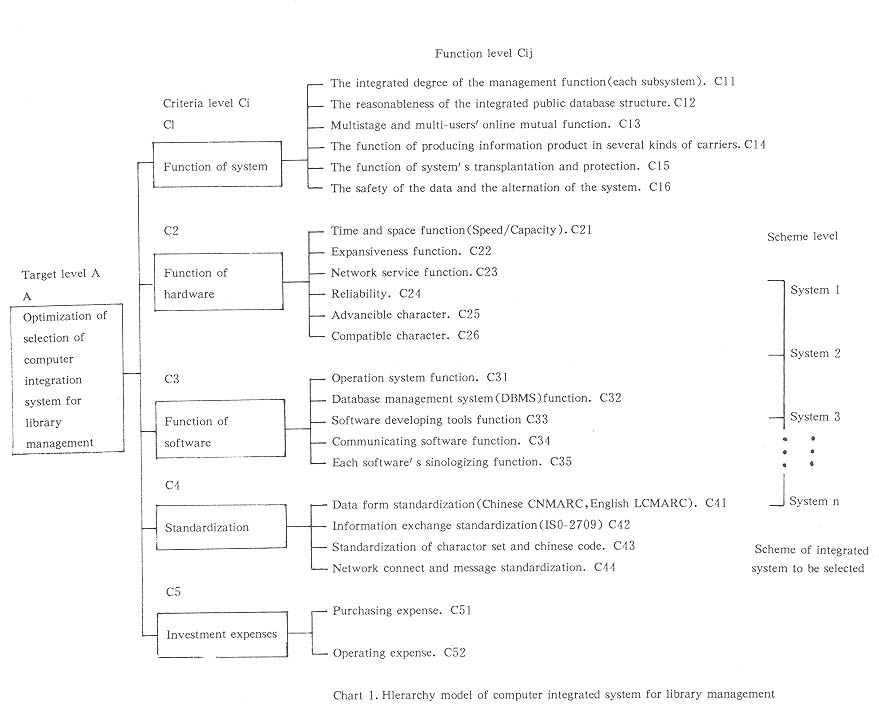
According to some reference materials, after many kinds of analysis, inducing and arrangement, the author sets up an AHP model (Chart 1).
The AHP model has three levels: A is the target level, selection of integrated system; Ci is the criteria level, (i=1,2,...,5), the criteria of integrated system selection evaluation, in five aspects, which contains 23 practical function targets (Cij); the lowest level is the scheme of integrated system to be selected.
Obviously, the weight (relative importance) of the five aspects of criteria and 23 function targets are different. To decide the weight which represents the relative importance of the whole system, we must use the AHP method in which the judgement matrix is set up by comparing their importance pairs. Then, solve it as an eigenvalue problem of the matrix to find out the relative important weight of a level compared with the upper one. After finding out the single queuing weight of each factor of the level compared with the upper one, sum up the weight of the upper level factors itself, then we can find out the relative important weight of the factors of the level compared with the weight of the whole upper level , that is the total queuing weight. In this way, from the upper one to the lower one, the weight which represents the importance of the lowest level relative to the highest level or as the queuing process of the system could be found. It can be referred to by the decider.
3. QUANTITATIVE HANDLING OF THE EVALUATING TARGET
According to the hierarchy structure model in Chart 1, deal with the target in quantativity. Using the highest level of the AHP model as the order, decide the weight of each factor compared with the upper level, that is, deciding the weight of Cij compared with Ci, which is Wij, and the weight of Ci compared with A, which is Wi.
3.1. The Procedure of the AHP method
A. Set up hierarchy structure model, divide the evaluation target into several different levels according to the problem need to be analyzed, such as target level, criteria level, and the lowest level (see Chart 1).
B. Make judgement matrix according to the relative importance of each factor.
B=[bij], satisfy
bij>0
bij = 1/bji, i,j = 1,2,...,n
bii = 1, i = 1,2,...,n
In AHP method, in order to make the decisive judgement quantitatively, the author makes judgement matrix numerically, the scaled method in Table 1, 1-9 is used.


D. Examining the uniformity of the judgement matrix.
In order to do this, we must find out its uniformity index CI, average stochastic uniformity index CI and stochastic uniformity rate CR, that is:
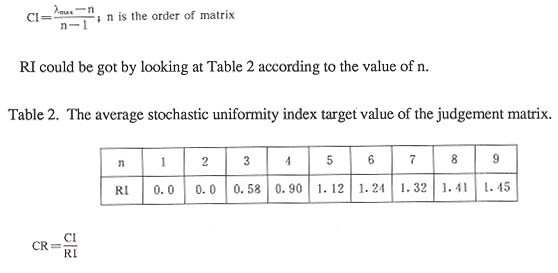
When CR < 0.10, the judgement matrix can be seen as having a satisfactory uniformity, that is, the weight vector is reliable. Otherwise, we must reconstruct the judgement matrix.
2). The AHP calculating result of each level weight of the target system
Optimization of the integrated system scheme is to evaluate the function of hardware and software of the whole system and its investment in all aspects. According to the theory of AHP and the method of scaling value, we should compare the system function hardware function, software function, the investment fee, and other factors in the same level. Then queue them according to their importance in the whole system. After that, compare them in pairs, determining their relative important weight. We could use two methods in determining the evaluation target weight. First, the specialist evaluating methods; second, the individual subjective evaluating method, that is, evaluating according to the individual's understanding. No matter which method is used, it must strictly depend on judging the basis of mathematics, that is, it must satisfy the requirement of stochastic uniformity rate CR < 0.10. Here we queue according to the above theory and compare the scaled value target in pairs. Finally, find the the weighted average. Make the judgement matrix according to the judgement of the relative importance of each target. We could decide each evaluation target criteria queuing weight by finding out the eigenvalue of the matrix.
We have done a simulating experiment on a PC-386
computer using the above method, and according to the given referent weight
value, have calculated the queuing value of each target. After finding
out the total queuing value of each target, times 1000, we could then get
the weighting value of each evaluating target. In this way, by totally
queuing levels, each Cij target value relative to the highest level weight
value could be found out. Totally queuing weight value could be used as
the optimizing order of the integrated system.
4. CONCLUSION
The AHP method is a relative evaluating mathematical method, this method contains both the people's subjective judgement and the objective criteria. Its judgement is easy, and its mathematical dealing is convenient. It is suitable to the comparison of several systems in finding out its selecting order.
Through inquiring, the author finds that it is absolutely
usable as an auxiliary in the decision of introducing and selecting the
computer integrated system for library management. The method could make
the qualitative and quantitative analysis synthetically so that we could
make a comprehensive evaluation of the integrated system to be selected.
REFERENCES
Saaty, T. L. (1980). The Analytic Hierarchy Process, McGraw Hill, Inc.
Wan Zhenshan. (1990). "Researching in evaluation target of integrated system of library," The 3rd Library Automation Meetin. (in Chinese)
Yu Fan. "A practical method of information research -- Introduction of AHP," Information Knowledge, 1989. (in Chinese)
Zhao Huanchen. (1986). AHP -- ¡ new convenient decision method. Beijing, Science Press. (in Chinese)