Edwin Karnitis
Latvian Academic Library
Riga, Latvia
e-mail: karnitis@lib.acadlib.lv
The creation of the Global Information Society has started in the world recent-ly. Latvian actions have to be rapid and efficient to join in this global process of informatization of national economy, research, education, and all spheres of activities.
This process is especially important for Latvia. We see the future of our national economy based on high technologies and production of knowledge-based and science-capacious products. Development of small and medium size enter-prises, academic reforms, integration of research and higher education are going on at present as well. Transition from command economy to the market one in Latvia and in other countries of Central and Eastern Europe is quite complex.
To achieve our national goals, the introduction and use of modern infor-mation technologies are essential. In order to have successful and fluent transition, availability of qualitative information -- i.e., precise, complete and timely information -- is an indispensable precondition for effective actions and optimal decision making. Presence of corresponding infrastructure for provid-ing of effective communication and quality information services is of top necessity. Old structures and institutions have to be reorganized, and some of them have to be abolished while new ones established.
Considerable changes proceed in Latvian informatics today. Up-to-date environment for information collection and processing, transmission and storage, browsing and search has been created. Development of telecommu-nication, networking and information technologies has radically changed all previous modes and notions of information delivery in Latvia. Today's approach to information support includes introduction of distributed and multiuser systems and teleaccess to data.
2. THE LATVIAN ACADEMIC LIBRARY
The Latvian Academic Library (LAL) is the main scientific and research infor-mation establishment in Latvia, and thus is involved closely in these current processes. At the present, the Library is in a transit situation. It is moving toward a modern information institution with dynamic information services, instead of the store house of traditional book stock.
In addition to ensuring of direct information services, the LAL involves the creation of national information infrastructure and is the provider of various electronic information services and information sources available in Latvian institutions. Meta information on them is collected to assess the currency, quality, reliability and availability of various information services. These data are accumulated in several printed and electronic directories, par-ticularly compiled for the European Commission in cooperation with The Euro-pean Association of Information Services (EUSIDIC) and Forschungscentrum Informationstechnik GmbH (GMD).
Currently, 69 institutions are active in the creation of information infrastructure and operational in various fields, including communication and networking services, information services, creating of electronic information sources, etc. Among them, there are 24 academic institutions, 15 government departments, 28 private/state commercial companies, and 2 public organi-zations.
All processes are dynamic in nature. At this time, several systems are under reconstruction at any given time period, not always with proper up-dating mechanisms. Some new databases may appear, and often they are not necessarily compatible to each other.
3. THE DEVELOPMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATION SERVICES IN LATVIA
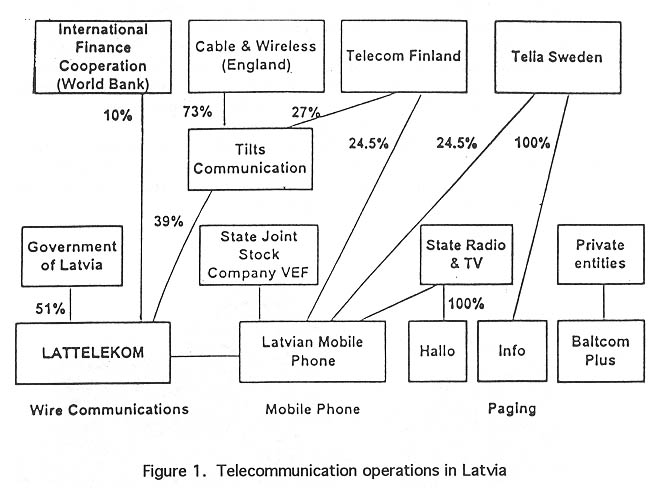
Fundamental reorganization of telecommunication services in Latvia was started in 1992. Real activities started by the founding of the Latvian-English-Finnish joint venture, Lattelekom, in January 1994 by winners of an international tender. Lattelekom is the monopolistic owner of all cable and wire network and communication equipment as well. According to the Telecommunication Law in Latvia, Lattelekom is the exclusive provider of all public telecommunication services -- international, national, within the State and local, as well as in cities. Only mobile communication services are permitted for other operators, who have to receive licenses from the Ministry of Communications. Figure 1 provides more information on the telecommuncation operators in Latvia.
Changes in all of the telecommunication systems in the country are being planned in accordance with the general telecommunication stabilization pro-gram during the next few years. It will be a big network, completely digital in order to provide up-to-date, basic and enhanced quality services to any subscriber in the country.

3.1. International Links
Reorganization also started with the modernization of international services. An international digital exchange had been put into operation in 1994. It pro-vides 4200 simultaneous telephone lines. Full automatic connection is ensured for subscribers of digital public network, and presently, operators are pro-viding ongoing connections for subscribers of the analog network.
Several international communication links have been created. Presently, surface satellite communication station provides 120 telephone lines to England via satellite EUTELSAT. Satellite communication will be provided with Southern Europe, Middle East and CIS also. Terrestrial microwave lines from Riga to Tallinn (Estonia) have been created and connected to the existing fiber-optic cable to Helsinki and Stockholm. Fiber-optic submarine cable from Ventspils (Latvia) to Stockholm (Sweden) was put into operation in the autumn of 1994. This is the main international line at present. All these together permit the provision of high quality and reliable international communications with more than 200 countries.
3.2. National and Local Links
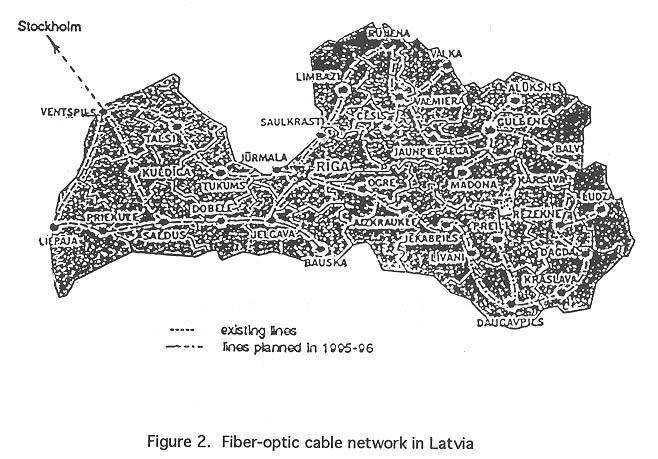
To provide up-to-date telecommunication services inside the country, a national fiber-optic cable network has been created. The first part of the network, the Western circle (Riga-Ventspils-Liepaja-Riga) and its connection to the Stockholm cable was completed in 1994. The completion of an Eastern circle is being planned for 1995-1996. This will connect with the telecommu-nication system of Russia and the rest of the inland connections. Figure 2 shows the fiber-optic cable network of the country.
The first digital local connection was made in the spring of 1995. Roughly 100,000 subscribers were connected in 1995 in Riga, Ventspils, and Cesis. Radio links are planned for use in the country, with real connections to digital networks in the country which started in 1995.
Also, installation of up-to-date public card and coin payphones for local and long distance calls are essential parts of the modernizing of telecommunica-tion services. The first payphones are connected and special Telecards are released for payment.
Improvement of a number of different services being provided to subs-cribers of digital network is being planned. First leased digital lines (128 kbps) coupled with facilities management are in operation. Introduction of ISDN communication systems will be started in 1996. It is planned to introduce 800-type service (free calls) during 1996 and Collect Call System after that (payment will be made by called up subscriber). At the same time the analog network will be developed also.
Digital connection requires a new payment method for Latvian subscri-bers of telecommunication services. Subscribers of analog network have to pay regular monthly subscription fees and special payment for long distance calls only, local calls are free of additional charges. Subscribers of digital network have to pay the time charge for local calls also. All payments are determined by independent Latvian Council of Telecommunication Tariffs to stave off exclusive prices. Reduced and economical tariffs exist besides the standard tariff.
Two systems of mobile telephone service develop in parallel today. Network of analog NMT-450 exchanges involves 67% of territory of Latvia with 89% of population. More than 10,000 subscribers are using this system. Digital GSM-900 system started to operate in January 1995 in Riga.
GSM is a better suitable system for regions with large density of popu-lation. It provides higher quality, possibility to ensure direct computer and fax connection, confidence of transmitted information, protection of unlicensed connection and different additional services (e.g., mail-box). Interchange agreements with mobile service operators of Germany, England, Scandinavian countries are signed at present, and agreements with operators of France and Italy will follow. These agreements permit subscribers from the mentioned countries use of their SIMs (Subscriber Identity Modules) and PINs (Personal Identification Numbers) in Latvia and vice versa.
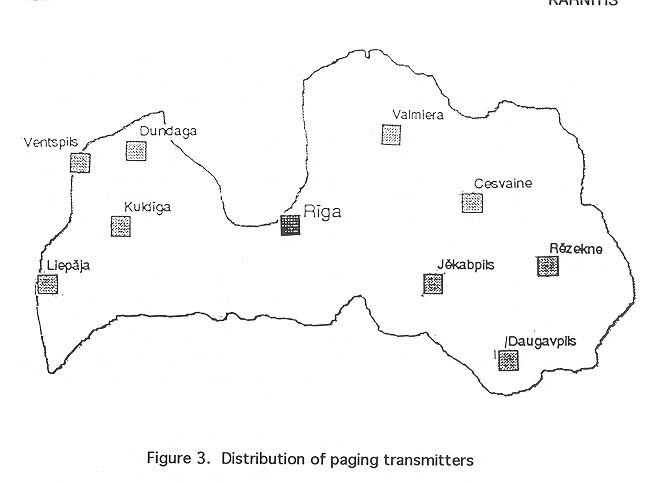
Paging is another radio communication service in which development is very dynamic today. Several paging systems provide service to most parts of the country. Systems accept messages in Latvian, English, and Russian. It is possible to deliver messages to Estonia and Moscow also. The number of alphanumerical pagers is 85% of total amount of pagers in Latvia. It is a result of a rather badly developed public telecommunication network at present. Fifty percent of total amount of subscribers are companies and institutions, the other 50% are private persons. Figure 3 shows the distribution of paging transmitters in Latvia.
4. INFORMATION NETWORKS AND DATA TRANSMISSION SERVICE IN LATVIA
With the general development of telecommunications described above, it be-came possible to have simultaneous progress in information networking. The communication network is created utilizing Lattelekom cable and wire network, characteristics of data network in a large measure depends on quality of the lines.
Latvian Academic and Research Network (LATNET) is the information network which connects research institutes, universities and other educational institutions, such as schools, education support centers and foundations, e.g., the Ministry of Education and Science etc. LATNET provides international connectivity to these entities under the management of the Institute of Mathe-matics and Computer Science of the Latvia University.
LATNET employs the most advanced high speed networking technology and the TCP/IP protocol which supports efficient internetworking in the heterogeneous Internet environment. Services available on the LATNET range from E-mail and remote database retrieval to high speed multimedia applica-tions, World Wide information retrieval (WWW, Gopher system) and World Wide team collaboration.
Along with academic applications, LATNET is supporting the spreading of Internet technology in other areas also, such as private communication, news dissemination, business contacts etc. LATNET is the real national information highway in Latvia today which provides high quality interconnected network and information services to all who need such services. Today, universities, research institutes and libraries, the Parliament of Latvia and other govern-mental institutions, banks and other commercial entities are subscribers of LATNET.
LATNET is connected to the international network system by several lines
at present (Figure 4 shows the Internet links established in Latvia). Riga-Stockholm
128 kbps fiber-optic line is the main international connection. The capacity
of the link can be expanded till 2-Mbps according to the growth of current
traffic. Berlin-Riga and Tallinn-Riga terrestrial 64-kbps links are used
mainly as backup international links. The last one and the Vilnius-Riga
28.8-kbps terrestrial line form the Baltic backbone network.
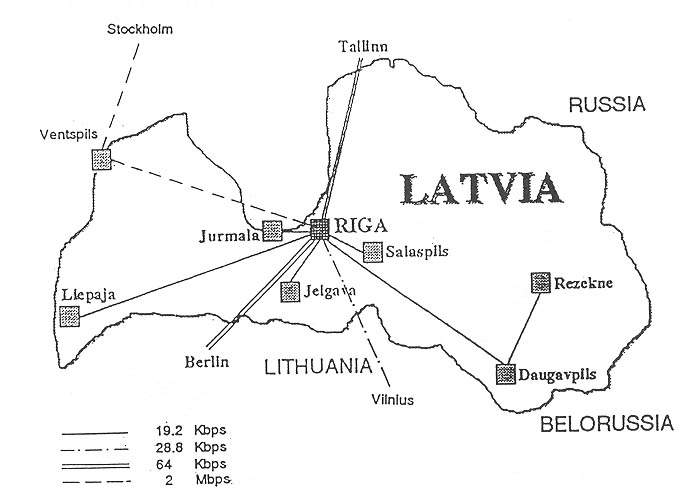
Figure 4. Internet links established in Latvia
Future development of LATNET is planned in several fields. It will be connected to the network by means of leased high-speed links, e.g., fiber-optic links, to all 26 administrative districts of Latvia. Several university buildings in Riga will be connected by the fiber-optic cable which will provide up to 100-Mbps connectivity among these buildings. Supercomputing and multimedia centers of the network have to be established for scientific computing by the various research institutions which require powerful computation resources in the fields of physics, biology, astronomy, chemistry, etc., for the preparation of various multimedia documents and for organization of distance learning over the network.
Several private companies provide global data transmission service on commercial basis (Figure 5) with some accent to financial and business infor-mation services and include direct connection with Russian networks, such as SovAM Teleport and EUnet/Relcom. Mainly, they operate in Riga and/or close to the first operating fiber-optic cable ring, Riga-Ventspils-Liepaja-Riga, in the western part of Latvia.
Figure 5. Distribution of commercial data transmission providers
5. ELECTRONIC INFORMATION SERVICES IN LATVIA
Telecommunications and networking are not an end in itself. They are tools to provide general availability to information. Access to international informa- tion sources is essential for various activities in the country, thus research and special libraries of national significance are the main resources for scien-tific, economic, technical and technological information including electronic information services in our country. Latvian Academic Library is the pioneer in providing electronic information services in Latvia and it remains the leader in this area among Latvian information institutions.
The first CD-ROM workstation was available in the LAL in 1992. Since then, the Library has continued to expand this informational service by means of increasing both the number of workstations and the acquisition of new CD-ROM databases. As of June 1995, more than 40 CD-ROM titles in all fields of science and technology were accessible for users in the Library. Currently, efforts are being made to disseminate information from CD-ROM databases via Local Area Network of the LAL and LATNET. Centralized CD-ROM service will be provided to researchers directly in their workplaces in universities and scientific institutions.
Successful introduction of CD-ROM information services is taking place today in other research libraries and in the National Library of Latvia. Sub-jects of databases are within the framework of general themes of the corres-ponding library.
Online service in Latvia started simultaneously with the extension of Internet and the creation of LATNET. This service expands virtually library stock, it gives access to the world's most significant scientific information sources and to the catalogues of the largest libraries.
Exactly for these objectives, the LAL was the first Latvian scientific institution connected via LATNET to Internet in 1993. The LAL has full Internet connection by means of 128-kbps leased line at present, and Local Area Net-work installed in the Library provides a sufficient number of on-line work-stations. In 1993 the LAL concluded license agreement with STN INTERNA-TIONAL online database system. As a result, more than 180 STN databases in all fields of science and technology are accessible for our users. Introduction of full text document delivery service via network is being planned for the near future.
All other major research libraries as well as the National Library of Latvia are now connected to LATNET in different ways (from dial-up to radio link) and can also provide Internet searching services to their patrons.
Widespread introduction of CD-ROM and online information services in major libraries is one of the most positive information developments in Latvia. These services quickly won popularity among Latvian specialists. Our experience at the LAL shows that the researchers and specialists are very interested in the use of electronic technologies, especially those involved in natural sciences and HiTech. Unfortunately, the specialists in social sciences and humanities display much less interest.
The LAL has developed the national policy of scientific and technical information services in Latvia, which has been approved by the Latvian Academy of Sciences. In accordance with this policy, CD-ROM and online technologies are used in Latvia as the main method for information browsing and search. To expand further use of electronic technologies, the LAL has had a number of information activities in addition to its direct information services. These include:
• presentations to introduce information companies and technologies,
• seminars on new information products, and
• training courses for information specialists and users.
6. CREATION OF ELECTRONIC INFORMATION SOURCES
Various electronic information sources containing significant Latvian informa-tion and information activities are worthwhile for authentic information support, since such information is necessary for both domestic specialists and the international community.
Currently, 57 organizations and 9 private persons are involved in the creation of electronic information sources in Latvia. These include research and academic institutions, as well as government and commercial organiza-tions. All institutions are operating in their corresponding fields. Creation of information sources is only one and most frequently not the main field of their activities. No one specialized electronic information producer and vendor is identified in Latvia at present.
At the end of 1995, there were 124 electronic sources identified, dealing with difference subject matters. They were of different types, ranging from CD-ROM, to online and offline databases, to online hypertext bulletin boards and WWW web sites. The largest number, 58 of the 124 (47% of the total) were online sources. Of these, 52 were bulletin boards and WWW sites. The other 6 were 5 online databases and one online library catalogue (in Latvian Academic Library).
WWW sites are the most popular online sources. Currently, more than 30 organizations and private persons have created their own sites and the number is growing rapidly. These sites present information on corresponding institu-tion and its activities. For example, the WWW site of the LAL contains news and general reference information on the Library, description on its history and collections, and links to databases and electronic catalogue of the LAL. Figure 6 is the Homepage of the LAL web site, while Figure 7 is a sample page of information from the site.
This information is accessible worldwide directly via several Latvian WWW title sites, via global lists and indexes List of W3 Servers, W3 Catalog, The Virtual Tourist, and Country maps from W3 servers in Europe. The LAL is included in LIBWEB -- List of Library information Servers via WWW.
Creation of databases is developing rapidly at the present too. Seventy-one various databases are identified in Latvia. The majority of databases (64 items) are off-line bases. They are accessible in institutions which are the

Figure 6. The LAL Homepage
producers of corresponding database, on stand-alone computer or via Local Area Network. The use of CD-ROM technology for production is not wide-spread in Latvia yet. Only two CD-ROM databases contain information on Latvia together with information on other Central and Easter European coun-tries.
Information accumulated in databases covers all types of fields, including:
• National economy, business, products - 23 databases
• Environmental information - 16 databases
• Dictionaries, catalogues, meta information - 11 databases
• Scientific information - 10 databases
• Statistical and regulatory information - 8 databases
• Culture, leisure - 3 databases

Figure 7. A sample page of information from the LAL web site
Fifty-eight databases are factographic (numerical and mixed) ones, 5 are full-text bases and 8 are bibliographic in nature. Forty-five databases are available since 1992 or later, 10 databases since 1990-1991 and 16 data-bases since 1990 and earlier. Some of those older databases are not updated regularly at this time. The languages used for these databases are:
• Latvian - 57
• English - 35
• Russian - 17
• German - 5
• Other - 4
A few databases contain information in two or more languages. The majority of databases contain information in different forms, numerical and graphic. Many of them calculate some statistical parameters -- the average quantity, deviations, errors, etc.
Latvian information has started to be included in worldwide database systems, particularly those of the United Nations database systems, such as INFOTERRA and AGRIS/CARIS, databases of World Data Center and the World Health Organization. The creation of the Latvian national nodes of various networks has also started. For example, the Latvian National Catalog Node of CIESIN and corresponding Database Nodes have started. One of these nodes will be organized by the LAL.
In order to provide worldwide access to gray literature published in
Latvia, the LAL has become a member of the European Association for Gray
Literature Exploitation (EAGLE). LAL is the Latvian National Centre and
in early 1996 will start data entry in gray literature database, SIGLE.
7. CONCLUSION
In addition to what was described above, many small data stores in different subject fields exist in research institutes and universities, in enterprises and governmental institutions, in personal computers of researchers. These files contain important and necessary data and information. It is possible to create new databases from these files. Clearly, one of the challenging tasks will be to create on-line databases from the off-line ones for future information access via the available data networks.
With the fast development of telecommunications, and data transfer and
proceeding systems, there is an urgent need for the Latvian information
specialists to be involved in the development of Lativia national information
infrastructure as soon as possible. There are many exciting opportunities
for the development of information services in Latvia today.