Graphics on the web are used in two general ways.
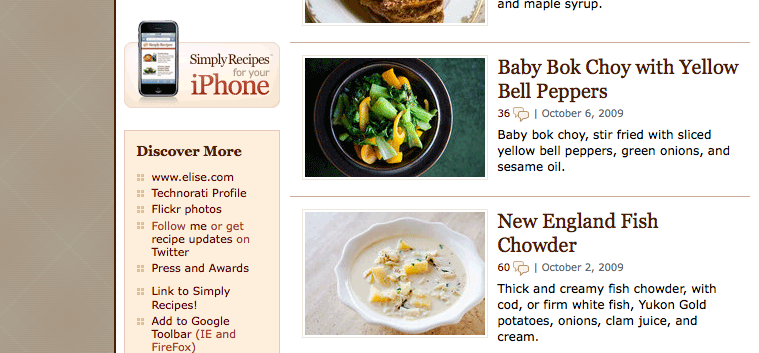
Here is a screenshot from Simply Recipes. There are quite a few graphics here.

The photographs, illustrations, and artwork are outlined in blue:
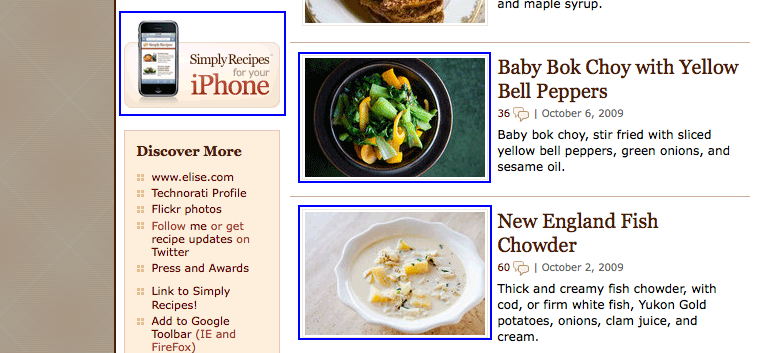
Images used to create structure and variety in the site outlined in red:
When possible, we follow these rules for using graphics:
img TagWe define images in HTML using the <img> tag.
The <img> has two required attributes
srchref attribute you've already used.altThe <img> tag is a self-closing tag. That means you put a slash at the end of it in XHTML.
Example:
<img src="images/molly.jpg" alt="A photograph of a Corgi puppy named Molly" />
In CSS we can set an image to be in the background.
This will display behind the normal text and other images in our HTML.
We can use this image to make a nice textured background.

div with the id of "demo" for this example.
div#demo {
background-image: url(texture.jpg);
}
Note: The URL of the image is relative to the CSS file, not the HTML.
The default setting for background images is for them to repeat both vertically and horizontally. We can change that with background-repeat.
div#demo {
background-image: url(texture.jpg);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
}
You can choose four settings for background-repeat:
You can also change the color of the background in addition to your image. In CSS, the specified background color will display under the background image.
div#demo {
background-image: url(texture.jpg);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-color: #C6AB6D;
}
Lastly, you can change the position of your background image.
You can use keywords, units of measurement, or percentages.

div#demo {
background-image: url(texture.jpg);
background-color: #C6AB6D;
background-position: 50px 100px;
}
You can define all of the above properties by simply using the shorthand background property.
div#demo {
background: #C6AB6D url(texture.jpg) repeat-x 50px 100px;
}