

View the web slides for web graphic image formats. Use the arrow keys to navigate.
The text below gives a little more context to the slides above.
Our sites are usually quite boring without the use of graphics.
The three most common file formats for graphics used on the web: JPG, GIF, and PNG. Each of these file formats are designed with a specific purpose in mind, so it is importawidth:47%;nt to understand the differences when we use them in our websites.
The JPG image format was designed to efficiently store and compress realistic images and artwork (both in color and greyscale). The JPG format does a very good job of compressing images with lots of colors and gradations in colors. Think of a JPG as a highly compressed photograph.
The JPG format is not capable of saving any transparencies. If transparency is needed in the background of your image, you must choose a different format.
When saving images in the JPG format, you can choose the level of compression to balance the file size and image quality. File size is directly related to the actual size (in pixels) of the image. A larger pixel size will always result in a larger file size.
Examples of images that should be saved in the JPG format:


The GIF and PNG image formats use what is called "index-color". They store a minimized color palette in the image file and keys to where those colors should be located in the image. File size for GIF and PNG images is generally related to the number of colors used. Commons numbers of colors are: 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256.
The GIF and PNG image formats are ideal for images with flat colors (no gradients) and hard edges. Common examples of these types of images are logos, logotypes, and illustrations without gradients.



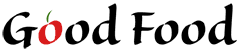
The GIF and PNG formats also both support transparency. If you need any level of transparency in your image, you must use either a GIF or a PNG.
GIF images (and also PNG) support 1-color transparency. This basically means that you can save your image with a transparent background.
Let's use the Good Food logo as an example. This has to be an image file because we're using fancy type and also a graphic of an apple in place of the a. We want our logo to sit on a light green background color. Here's our background color we're saving the logo on.
If we saved the logo as a JPG, we'd be stuck with some kind of background color.
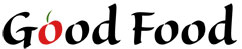
JPG will not give us transparency
Obviously, having a background color in this situation is not ideal. If we save the image as a GIF, we can use a transparent background color.
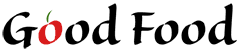
The GIF give us a transparent background. Notice the ring around the text.
Using a GIF image with a transparent background allowed us to put our image on a different color background. Notice the white ring around the image though. This is because GIF images can only use 1-color transparency. We cannot slowly fade to transparency. There will always be a colored ring around the image. We can change the color of the ring, but this means we must know ahead of time what color background we are going to be using.
The PNG file format is capable of saving variable levels of transparency. This is known as the alpha channel. Using variable transparency, we can actually use transparencies as a gradient.
The easiest way to demonstrate variable transparency is through an example. Below is the same image twice, on two different background colors.


Notice how the background color simply fades into the picture.
Going back to our Good Food logo, we can use the same technique to make sure our logo blends to any background color.
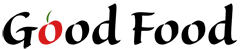
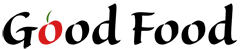
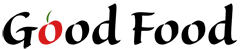
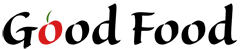
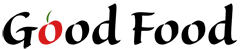
The PNG format comes in two varieties: 8-bit and 24-bit.
The 8-bit format functions just like a GIF file. It uses index-color and can provide one color transparency. This is the format that you should use most of the time when saving your images as PNG files.
The 24-bit format functions more like a JPG file. You can save photographs using this format, but in general the file size is bigger than a JPG, so you should use a JPG instead. If you want to use variable transparency, you must save your file as a 24-bit PNG. In general, the only time you use 24-bit PNG files on the web is for images that require variable transparency.

You might be wondering at this point how to know when to use a GIF or a PNG. GIF is an older file format going back to the early 1990's. It used to be used for really obnoxious image animations, which have experienced a resurgence in popularity in recent years. GIF is the only file format that can accomplish this.
The PNG format is the newer and better format. The PNG format uses a better compression scheme than GIF so the file sizes are generally smaller. Additionally, PNG images can be further compressed using a compression tool like Tiny PNG or ImageOptim which is installed on the lab computers.
Unless you want to animate a cat throwing a dog, or do some sort of artsy loop thing, use the PNG format instead of GIF.
Google has been developing a modern image format designed for the web called WebP. While it's not quite in common usage yet, you may see it in the wild. The new format holds some promise.